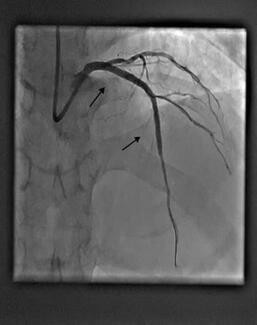
Expanding a Multi-Specialty ASC to Include a Cardiac Service Line
Cath Lab Digest talks with Dr. Sarang Mangalmurti of Bryn Mawr Medical Specialists in Bryn Mawr, Pennsylvania. Dr. Mangalmurti shares his experience opening an ambulatory surgical center (ASC) and how he expanded it to include a cardiac service line. This episode is also available on Spotify and Apple Podcasts!
This podcast is sponsored by Philips OBL and ASC Solutions, SymphonySuite.
⬇️ ⬇️ ⬇️
Dr. Mangalmurti's Key Themes & Takeaways:
1. Why Add Cardiac Services to an ASC?
-
More cardiac care is moving to the outpatient setting as patients look for convenience, lower costs, and quicker recovery.
-
Hospitals are stretched, and ASCs can safely take on appropriate lower-risk cardiac cases.
-
Cardiologists and other specialists want more control over workflow, scheduling, and patient experience.
Bottom line: For the right patients, ASCs offer a high-quality, efficient, and cost-effective alternative to the hospital.
2. Building a Cardiac Service Line
A. Regulatory Considerations
-
Rules vary widely by state, and certification requirements can be strict.
-
Programs often start with diagnostic caths, peripheral vascular work, or EP studies.
-
PCI eligibility requires meeting specific safety, transfer, and volume standards.
B. Making the Business Case
-
Start with market analysis—patient demographics, referral patterns, and local hospital dynamics.
-
Assess expected case types: diagnostics, peripheral, EP, implants, and potential for future coronary work.
-
Develop a financial plan covering equipment, staffing, supplies, and reimbursement mix.
Takeaway: Every market is different; a solid business model is critical before launching.
3. Facility & Equipment Needs
-
Choosing the imaging system (fixed vs. mobile) is a major early decision.
-
The physical space must support cardiac procedures: lead-lined rooms, appropriate electrical and HVAC capacity, emergency equipment, and adequate recovery bays.
-
Inventory must accommodate multiple specialties and high-acuity cardiac supplies.
Takeaway: Plan for where the program is heading, not just the initial launch.
4. Staffing & Training
-
A strong team blends ASC efficiency with true cath lab experience.
-
Key roles include cardiac-trained RNs, radiologic technologists, cardiovascular technologists, and ACLS-certified staff.
-
Ongoing training, competency checks, and cross-training are essential.
Takeaway: Finding and developing staff with real cardiac expertise is often one of the toughest parts.
5. Workflow & Procedure Management
-
Pre-procedure steps include risk assessment, imaging review, and medical optimization.
-
During cases, clear team roles, efficient turnover, radiation safety, and sedation protocols are critical.
-
Post-procedure care focuses on monitoring, meeting discharge criteria, and ensuring timely follow-up.
Takeaway: Workflows must mirror hospital-level safety while preserving ASC speed and efficiency.
6. Safety & Emergency Preparedness
-
A transfer agreement with a nearby hospital capable of PCI and cardiac surgery is mandatory.
-
Teams need well-defined pathways for managing instability, vascular issues, arrhythmias, and other complications.
-
Regular simulation drills help maintain readiness.
Takeaway: Emergency preparedness isn’t optional, but is central to safe cardiovascular care in an ASC.
7. Financial & Reimbursement Realities
-
Success depends on understanding CMS policies, commercial payer expectations, and bundled payment structures.
-
Cardiac cases come with significant supply costs; strong vendor relationships and smart purchasing strategies matter.
Takeaway: Cardiac ASCs can be financially successful, but only with disciplined cost management.
8. Physician Engagement & Culture
-
Physicians set the tone for case volume, safety, and overall operations.
-
Involving them early in planning strengthens alignment and program sustainability.
Takeaway: Culture and collaboration are just as important as capital investment.
9. The Future of Cardiac Care in ASCs
-
More cardiac procedures continue shifting to outpatient settings.
-
Hybrid ASC-OBL models are becoming more common.
-
CMS is steadily expanding the list of allowable procedures.
-
Patient preference for same-day, convenient care will only accelerate this trend.
Overall takeaway: Outpatient cardiac care is growing quickly, and ASCs that move early and build programs the right way are helping define the future standard.
Find More:
Cardiovascular Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) Topic Center
Podcasts: Cath Lab Conversations
Grand Rounds With Morton Kern, MD